请关注公众号


上文 哈希链表和LRU算法 介绍了内存管理算法中的LRU算法,本文介绍另一种管理内存的算法——LFU算法(最不经常使用算法)。
LRU(最近最少使用算法) 和 LFU(最不经常使用算法)的区别:
前者是优先淘汰内存中最久没有使用过的数据,其淘汰依据是某个数据距离上次被访问的时间(或者说上一次被使用的时间有多久);
后者是优先淘汰内存中使用次数最少的数据,淘汰依据是某个数据被使用的频率或次数。
下面我们直接通过力扣的一道题目来了解LFU算法。
力扣460. LFU 缓存
请你为 最不经常使用(LFU)缓存算法设计并实现数据结构。
实现 LFUCache 类:
LFUCache(int capacity) - 用数据结构的容量 capacity 初始化对象
int get(int key) - 如果键存在于缓存中,则获取键的值,否则返回 -1。
void put(int key, int value) - 如果键已存在,则变更其值;如果键不存在,请插入键值对。当缓存达到其容量时,则应该在插入新项之前,使最不经常使用的项无效。在此问题中,当存在平局(即两个或更多个键具有相同使用频率)时,应该去除 最近最久未使用 的键。
注意「项的使用次数」就是自插入该项以来对其调用 get 和 put 函数的次数之和。使用次数会在对应项被移除后置为 0 。
为了确定最不常使用的键,可以为缓存中的每个键维护一个 使用计数器 。使用计数最小的键是最久未使用的键。
当一个键首次插入到缓存中时,它的使用计数器被设置为 1 (由于 put 操作)。对缓存中的键执行 get 或 put 操作,使用计数器的值将会递增。

题目给出LFU数据结构框架如下
type LFUCache struct {
}
func Constructor(capacity int) LFUCache {
}
func (this *LFUCache) Get(key int) int {
}
func (this *LFUCache) Put(key int, value int) {
}
/**
* Your LFUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* obj := Constructor(capacity);
* param_1 := obj.Get(key);
* obj.Put(key,value);
*/
分析:
我们根据Get和Put的需要设计数据结构,为此需要绘制Put的流程图(Get涉及到的问题Put都会涉及到,因此只绘制Put的流程图即可)。假设一个在缓存中的数据的键、值和访问次数为key、value和freq。
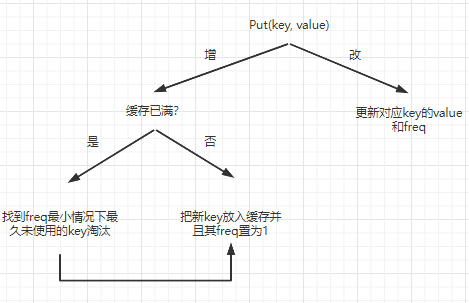
根据这个流程图我们知道以下需求:
0、根据不同freq(数据的访问次数)对所有数据进行分级
LFU算法要求优先淘汰缓存中访问次数最小的数据,如果有多个数据它们的访问次数都最小,则按照最近最少使用算法从访问次数最小的这些数据中选择其中最久未被访问的数据进行淘汰。
为了满足这个需求,需要为每种不同访问次数的数据创建一个链表队列(称为 freqLink),链表的节点按数据的访问时间远近排序。
freqLink链表其实就是 优先级队列,不同freq代表不同的优先级,每个相同优先级的数据都放在同一个队列中。
每个节点存储 key 和 value,以及前后指针。节点对象和链表对象分开管理,而不是用头结点对象表示链表。
1. 根据key找到value
可以使用哈希表 kvMap 记录key和 freqLink链表节点的映射关系,形成多个哈希链表。
2. 找到最小freq和最小freq下最久未使用的key
使用一个变量 minFreq 记录最小的freq;
使用一个哈希表 flMap 记录 freq 和 freqLink 的映射关系,flMap 的键就是 freq, 值是双向链表 freqLink 的地址。
3. 更改某个key的freq
只需将key对应的node从某个优先级的 freqLink 队列取出,放到另一个优先级队列即可。
整个数据结构如下图:
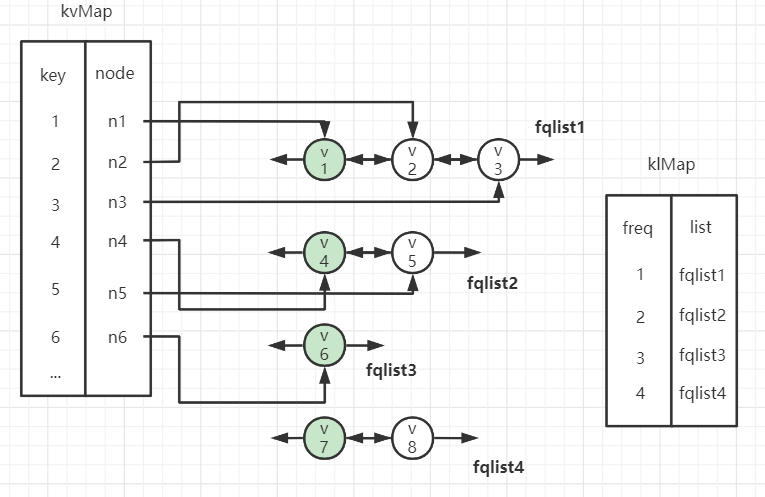
为了得知某个key的freq是多少,需要根据key查到node,再从node读取freq。
但我没有直接把freq作为成员写入到node节点中,而是把freq作为链表的成员,node则增加一个ListAddr的成员指向其所属的链表,在通过ListAddr.Freq获取节点的使用次数。
这样做的原因是一条链表的所有node的使用次数肯定是相同的,作为链表的成员属性更合适,如果每个node都存一个freq,就显得有点数据冗余。
代码实现如下:
type LFUCache struct {
KvMap map[int]*LFUNode
KlMap map[int]*LFULinkedList
Length int // 当前缓存的key的个数
Capacity int // 最大缓存的key个数
MinFreq int // 当前最小访问次数
}
func Constructor(capacity int) LFUCache {
kvMap := make(map[int]*LFUNode)
klMap := make(map[int]*LFULinkedList)
cache := LFUCache{
KvMap: kvMap,
KlMap: klMap,
Capacity: capacity,
}
return cache
}
func (this *LFUCache) Get(key int) int {
if this.Capacity == 0{
return -1
}
node, ok := this.KvMap[key]
if !ok{
return -1
}
this.updateKeyFreq(key)
return node.Val
}
func (this *LFUCache) Put(key int, value int) {
if this.Capacity == 0{
return
}
node, ok := this.KvMap[key]
if ok{ // 修改
node.Val = value
this.updateKeyFreq(key)
return
}
// 新增
if this.Length >= this.Capacity{ // 需要淘汰某个节点
this.removeLeast() // 淘汰掉使用次数最少的key
}
this.addKey(key, value)
}
// 更新某个key的使用次数
func (this *LFUCache) updateKeyFreq(key int){
node := this.KvMap[key]
myList := node.ListAddr
freq := myList.Freq
myList.remove(node)
if myList.Length == 0{ // 如果node之前所在的链表的数量为0,则从KlMap中注销这个链表
delete(this.KlMap, freq)
if freq == this.MinFreq{ // 如果注销的链表的使用次数刚好是最小使用次数,则更新最小使用次数
this.MinFreq++
}
}
freq++ // 节点使用次数+1
this.addNodeToFreq(node, freq)
}
// 将某个节点添加到某个freq的链表
func (this *LFUCache) addNodeToFreq(node *LFUNode, freq int){
newList, ok := this.KlMap[freq]
if !ok{
newList = initLFULinkedList(freq)
this.KlMap[freq] = newList
}
newList.appendNode(node)
}
func (this *LFUCache) addKey(key, value int){
this.MinFreq = 1 // 更新最小使用次数为1
newNode := InitLFUNode(key, value, nil)
this.addNodeToFreq(newNode, 1) // 新增新节点到链表,并且使用次数置为1
this.KvMap[key] = newNode
this.Length++
}
// 淘汰掉使用次数最少的key
func (this *LFUCache) removeLeast(){
leastList := this.KlMap[this.MinFreq] // 使用次数 最少的链表
deleteNode := leastList.shift() // 移除掉相同使用次数下最久未使用的节点
delete(this.KvMap, deleteNode.Key)
this.Length--
// 如果leastList没有Key,则从KlMap中注销
if leastList.Length == 0{
delete(this.KlMap, this.MinFreq)
}
}
链表节点对象
type LFUNode struct{ // 值为整型的链表节点
Prev *LFUNode // 向前指针
Next *LFUNode // 向后指针
Key int // key
Val int // 值
ListAddr *LFULinkedList // 节点所在的链表
}
func InitLFUNode(key, val int, myList *LFULinkedList) *LFUNode{
node := LFUNode{}
node.Key = key
node.Val = val
node.ListAddr = myList
return &node
}
func (this *LFUNode) setLFUNodeList(myList *LFULinkedList){
this.ListAddr = myList
}
双向链表对象
/** 双向链表 **/
type LFULinkedList struct{
Head *LFUNode // 头部节点
Tail *LFUNode // 尾部节点
Length int // 节点数
Freq int // 链表的权重,即节点的使用次数
}
func initLFULinkedList(freq int) *LFULinkedList{
linkedList := LFULinkedList{Freq: freq}
linkedList.Head = InitLFUNode(0, 0, &linkedList) // 虚拟头尾节点
linkedList.Tail = InitLFUNode(0, 0, &linkedList)
linkedList.Head.Next = linkedList.Tail
linkedList.Tail.Prev = linkedList.Head
return &linkedList
}
// 移除某个节点
func (ll *LFULinkedList) remove(node *LFUNode) *LFUNode{
if node.Prev != nil{
node.Prev.Next = node.Next
}
if node.Next != nil {
node.Next.Prev = node.Prev
}
ll.Length--
//node.setLFUNodeList(nil)
return node
}
// 从头部弹出一个节点
func (ll *LFULinkedList) shift() (deleteNode *LFUNode){
if(ll == nil || ll.Length == 0){
return
}
return ll.remove(ll.Head.Next)
}
// 往后插入一个节点
func (ll *LFULinkedList) append(key, val int) *LFUNode{
node := InitLFUNode(key, val, ll)
ll.appendNode(node)
return node
}
func (ll *LFULinkedList) appendNode(node *LFUNode) *LFUNode{
node.setLFUNodeList(ll)
lastNode := ll.Tail.Prev
lastNode.Next = node
ll.Tail.Prev = node
node.Prev = lastNode
node.Next = ll.Tail
ll.Length++
return node
}
func (ll *LFULinkedList) getHead() *LFUNode{
if ll.Length == 0{
return nil
}
return ll.Head.Next
}
func (ll *LFULinkedList) getTail() *LFUNode{
if ll.Length == 0{
return nil
}
return ll.Tail.Prev
}
上述解法中使用了2个hashmap,kvMap保存了key-node的映射,klMap保存了key-freqList的映射。
实际上,上述做法可以继续优化。
klMap的作用是访问某个数据A,导致需要将A节点从某个访问次数的链表X转移到链表Y时,可以快速定位到链表Y。
可以使用一个双向链表 freqSortList 简称 fsl 链表。fsl链表的节点有两个属性:freqListAddr属性存储某个访问次数下的freqList地址;freq属性存储该freqList的访问次数。fsl链表按freqList的访问次数由小到大的顺序存放节点。
此时将A节点从某个访问次数的链表X转移到链表Y的复杂度依旧是O(1),因为X和Y在 fsl 链表上是相邻的。使用fsl链表代替klMap是一种优化,因为相同数据量而且没有随机查询的需求下,链表在时间和空间占用上肯定都小于hashmap。
fsl链表在逻辑上相当于是一条线将每个freqList链表的头结点纵向链接了起来:
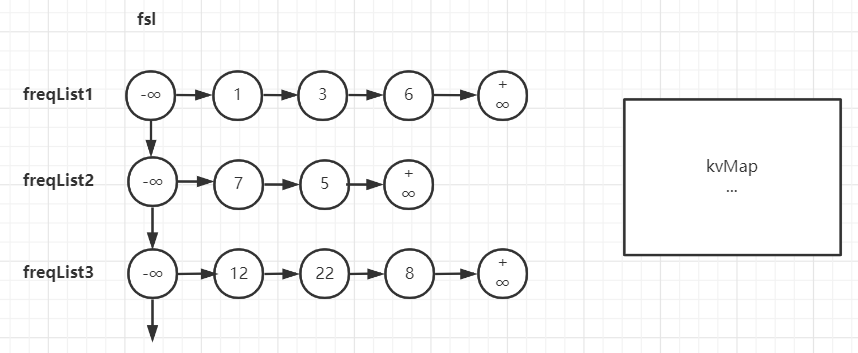
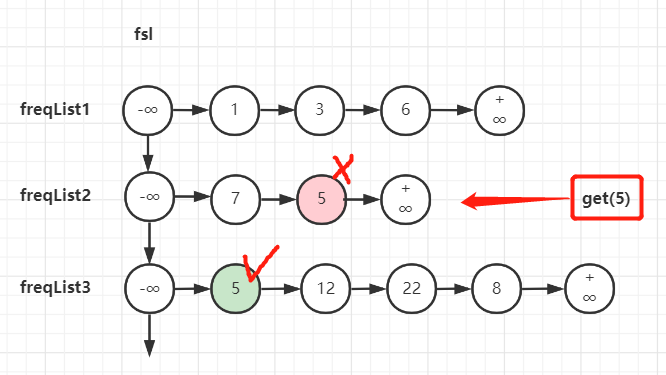
如此一来node节点需要存储节点的访问次数freq,而freqList可以不用存储节点的访问次数freq。
代码实现如下:
import "container/list"
type LFUCache struct {
kvMap map[int]*list.Element // key-lfunode
fsl *list.List // fsl的node是fslNode
capacity int // 缓存容量
nums int // 缓存数据实际数量
}
type lfuNode struct{
key, value, freq int
myFslElement *list.Element
}
func InitLfuNode(key, value int, fslElement *list.Element) *lfuNode{
return &lfuNode{key:key, value: value, freq:1, myFslElement: fslElement}
}
func (this *lfuNode) getLfuList() *list.List{
return this.myFslElement.Value.(*fslNode).lfuList
}
type fslNode struct { // 一个 fslNode 代表一条 lfuList
freq int
lfuList *list.List // 里面的node是lfuNode, lfuList不可见,只能通过方法访问
}
func InitFslNode(freq int) *fslNode{
return &fslNode{freq: freq, lfuList: list.New()}
}
func (this *fslNode) getLfuList() *list.List{
return this.lfuList
}
func LFUConstructor(capacity int) LFUCache {
return LFUCache{
kvMap: make(map[int]*list.Element),
fsl: list.New(),
capacity: capacity,
}
}
func (this *LFUCache) Get(key int) int {
lfuElement := this.getLfuElement(key)
if lfuElement == nil{
return -1
}
lfuNode := lfuElement.Value.(*lfuNode)
this.addFreq(lfuElement, lfuNode)
return lfuNode.value
}
func (this *LFUCache) getLfuElement(key int) *list.Element{
if _, ok := this.kvMap[key]; !ok{
return nil
}
return this.kvMap[key]
}
func (this *LFUCache) addFreq(ele *list.Element, node *lfuNode){
// 更改原本节点的freq
nextFslElement := this.findNextLfuList(node)
newLfuList := nextFslElement.Value.(*fslNode).getLfuList()
this.removeLfuElementFromList(ele, node)
node.freq++
newLfuList.PushBack(node)
node.myFslElement = nextFslElement
}
// 寻找比 node.freq 大1的lfuList链表
func (this *LFUCache) findNextLfuList(node *lfuNode) (fslElement *list.Element){
myFslElement := node.myFslElement
nextFslElement := myFslElement.Next()
if nextFslElement == nil{
// 创建一个新的lfuList
return this.createNewLfuList(node.freq+1, myFslElement)
}
nextFslNode := nextFslElement.Value.(*fslNode)
if node.freq + 1 == nextFslNode.freq{
return nextFslElement
}
// 创建一个新的lfuList
return this.createNewLfuList(node.freq+1, myFslElement)
}
func (this *LFUCache) createNewLfuList(freq int, prevFslElement *list.Element) (fslElement *list.Element){
nextFslNode := InitFslNode(freq)
if prevFslElement == nil{
return this.fsl.PushFront(nextFslNode)
}else{
return this.fsl.InsertAfter(nextFslNode, prevFslElement)
}
}
func (this *LFUCache) removeLfuElementFromList(ele *list.Element, node *lfuNode){
lfuList := node.getLfuList()
lfuList.Remove(ele)
if lfuList.Len() == 0{
this.fsl.Remove(node.myFslElement)
}
}
func (this *LFUCache) Put(key int, value int) {
// 修改数据
lfuElement := this.getLfuElement(key)
if lfuElement != nil{
lfuNode := lfuElement.Value.(*lfuNode)
lfuNode.value = value
this.addFreq(lfuElement, lfuNode)
return
}
// 新增数据
if this.capacity <= this.nums{
if this.capacity == 0{
return
}
// 淘汰掉最少使用的节点
this.removeLeastNode()
}else{
this.nums++
}
var fslElement *list.Element
if this.fsl.Len() == 0{
fslElement = this.createNewLfuList(1, nil)
}else{
minFslElement := this.fsl.Front()
minFslNode := minFslElement.Value.(*fslNode)
if minFslNode.freq == 1{
fslElement = minFslElement
}else{
fslElement = this.createNewLfuList(1, nil)
}
}
lfuNode := InitLfuNode(key, value, fslElement)
this.kvMap[key] = fslElement.Value.(*fslNode).lfuList.PushBack(lfuNode)
}
func (this *LFUCache) removeLeastNode(){
// 找到freq最小的lfuList
minFslElement := this.fsl.Front()
minFslNode := minFslElement.Value.(*fslNode)
minLfuList := minFslNode.lfuList
minLfuNode := minLfuList.Front()
delete(this.kvMap, minLfuNode.Value.(*lfuNode).key)
minLfuList.Remove(minLfuNode)
if minLfuList.Len() == 0{
this.fsl.Remove(minFslElement)
}
}
